The SKLRD Research Team Led by Wang Jian Discovers that Piezo1 is Involved in the Molecular Mechanism of Pulmonary Hypertension Caused by High Pulmonary Blood Flow
2022-08-19965Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a group of syndromes characterized by progressive increases in pulmonary artery pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance, eventually leading to right heart failure and even death. Pulmonary hypertension is pathologically based on pulmonary vascular remodeling caused by various factors, and hemodynamic and shear stress are two long-neglected important factors of pulmonary vascular remodeling. Piezo Type Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Component 1 (Piezo1) is an important mechanosensitive channel related to vascular remodeling, which can be activated by various forms of mechanical stimulation (e. g., flow shear, membrane stretching).
Recently, the SKLRD team led by professor Wang Jian has published an article entitled “Upregulation of Mechanosensitive Channel Piezo1 Involved in High Shear Stress-induced Pulmonary Hypertension” in the international journal Thrombosis Research (IF=10.407). The study shows that Piezo 1 activated by pulmonary hemodynamics of LPAL-induced PH plays an important role in the pulmonary artery, pulmonary tissue, and right ventricular remodeling in rats. The study will provide new therapeutic targets for PH and right heart disease caused by increased blood flow, such as left-to-right shunt congenital heart disease and CTEPH.
This paper is the first in vivo study of the function and mechanism of Piezo 1 under high shear stress-induced pulmonary hypertension. The research team led by Wang Jian developed 2-week and 5-week models of pulmonary hypertension in rats through left pulmonary artery ligation (LPAL) to simulate pulmonary hypertension induced by high flow and hemodynamic stress. Piezo 1 expression was upregulated in the whole lung tissues of LPAL rats compared with the rats of sham control group. Piezo1 upregulation was observed in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) of LPAL-2w and LPAL and LPAL-5w rats, which was associated with an increase in cytosolic Ca2 + concentration ([Ca2 +] cyt). It was discovered in the mechanism study that upregulation of Piezo 1 in PASMCs of LPAL rats was directly related to Yes-related protein (YAP) / TEA domain transcription factor 4 (TEAD4); and upregulation of pulmonary artery endothelial cells (PAECs) in Piezo 1 was related to the transcriptional regulation of RELA (p65) and lung inflammation. This study revealed a combined role of Piezo 1 in regulating PASMCs and PAECs, coordinated by different cell signaling pathways, leading to pulmonary vascular remodeling in LPAL-pulmonary hypertension rats, providing new insights into the cell-type-specific pathogenic role of Piezo1 in shear stress-related experimental pulmonary hypertension.
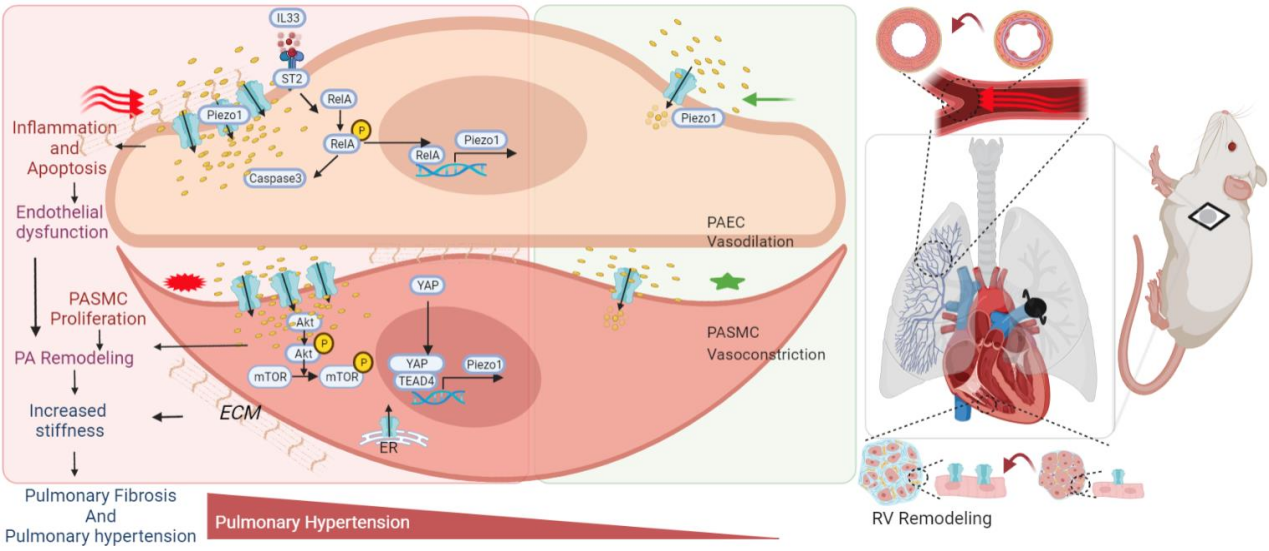
This paper clarifies that Piezo 1 is involved in the regulation of pulmonary vascular remodeling mechanism in PH induced by high pulmonary blood flow through the differential regulation of PASMCs and PAECs
Original paper:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0049384822003395