Researcher Zhou Rong’s team publishes a cover article in Virologica Sinica to analyze the characteristics and risk factors of severe adenovirus in children
2022-07-21913In June 2022, the team led by research fellow Zhou Rong and associate research fellow Liu Wenkuan from SKLRD published a cover article titled “Analysis of severe human adenovirus infection outbreak in Guangdong Province, southern China in 2019” in the journal Virologica Sinica (IF: 6.947), which analyzed the risk factors of severe adenovirus infection in children.

Between 2018 and 2019, a severe pediatric human adenovirus (HAdV) infection outbreak occurred in southern China. The article screened 18 respiratory pathogens in 1,704 children (14 years old) hospitalized for acute respiratory diseases in Guangzhou, China in 2019. A total of 151 (8.9%) patients tested positive for HAdV; 34.4% (52 / 151) had serious disease. HAdV infection occurs throughout the year, with a peak in the summer. The median age of the patients is 3.0. Compared with non-severe infection patients, patients with severe HAdV infection witnessed an increase in 12 clinical indicators (P≤0.019) and a decline in 4 indicators (P≤0.007). There was no significant difference in the age or gender distribution of patients with different HAdV infection severity (P>0.05); However, composite diseases and HAdV-coinfection were significantly different in patients with different HAdV infection severity (P<0.05). The main epidemic types of HAdV infection were HAdV-3 (47.0%, 71/151) and HAdV-7 (46.4%, 70/151). However, the severe case rate of HAdV-7 patients (51.4%) was significantly higher than that of HAdV-3 patients (19.7%) and other patients with HAdV types (20%) (P<0.001). Genomic accession of 13 hadv-7 isolates at different points of time= "" no.= "" p= ""> 0.05); the HAdV-7 isolated strain showed greater virulence and infectivity compared with HAdV-3 (P<0.001). According to the study, composite diseases, HAdV-coinfection, and the high virulence and infectivity of HAdV-7 are the key risk factors for severe HAdV infection; these data facilitate the treatment, control, and prevention of HAdV infection.
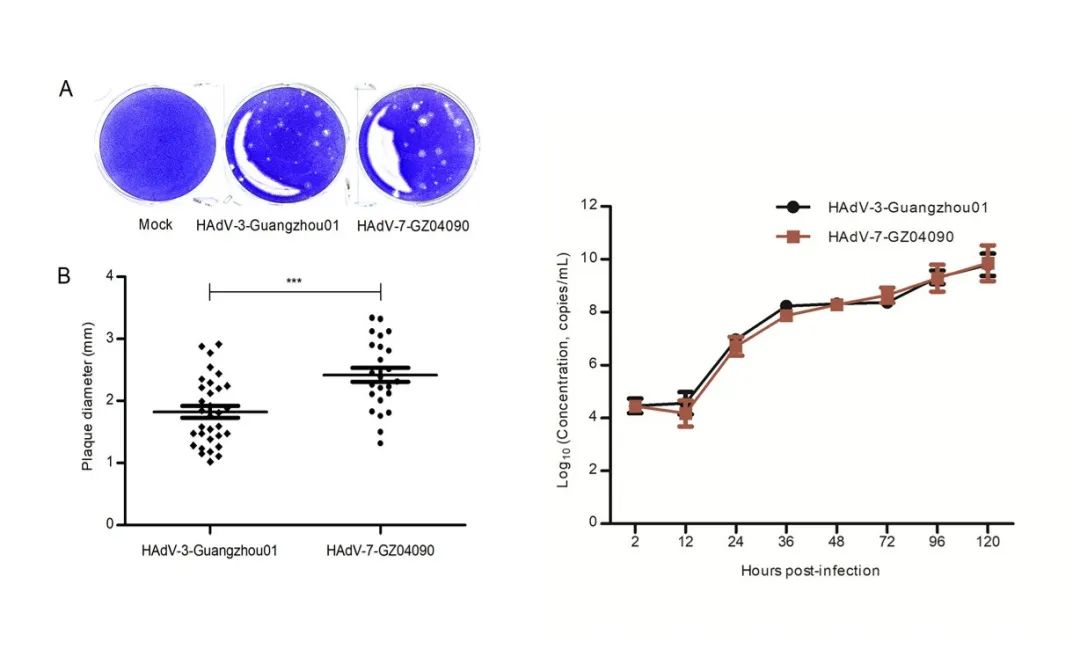
The HAdV-7 isolated strain shows greater virulence and infectivity compared with the HAdV-3 epidemic strain (P <0.001); both show a similar proliferation curve (P> 0.05)