Gold Gained after the Sandstorm Calms--Unit Drugs with Origin of Chinese Medicine: New Hopes for the Research and Development of PH Drugs
2021-12-011146Background
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a multi-factor hemodynamic disease characterized by an abnormal rise of pulmonary artery pressure. Its prominent pathological features include pulmonary artery endothelial injury, inflammatory cell infiltration, pulmonary artery smooth muscle cell dysplasia, which has facilitated the pulmonary vascular remodeling and obstruction and abnormal vascular contraction, thereby increasing the burden of pulmonary heart and affecting its functions, leading to death. At present, the main treatment strategies for PH mainly include supportive treatment with diuretic and oxygen therapy, targeted drug therapy, and surgical treatment such as heart and lung transplantation. Among them, the drugs approved to be used in the clinical treatment of PH include Endothelin receptor antagonist, phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor, soluble guanylyl cyclase agonist, protracyclin analogue and protracyclin receptor agonist. Though compared with the placebo group, these drugs can relieve PH by diastole of PA and inhibition of pulmonary vascular remodeling, yet they cannot increase the long-term survival rate of the patients. Besides, they are expensive, which limits their clinical application. Therefore, it is of very important significance to search for new therapeutic targets for PH and develop new effective, cheaper and multi-target drugs.
In recent years, the researchers have screened several effective units with a prospect for the treatment of PH from traditional Chinese medicines. This review summarizes the researches on the treatment of PH with these effective units, with an expectation to provide some new ideas on the research and development of new drugs for PH.
Research method
We’ve selected the databases PubMed, Cochrane Library, Clinical Trials, Embase, Ovid and ScienceDirect, retrieved the literature related with the treatment of PH with related units from Chinese medicine published from 2010 to March 2020 and summarized the related pharmacological action of every drug. We’ve screened the researches of 27 compounds of nine categories and made a review based on the chemical classification of natural drugs.
Unit drugs and mechanism with therapeutic effect for PH
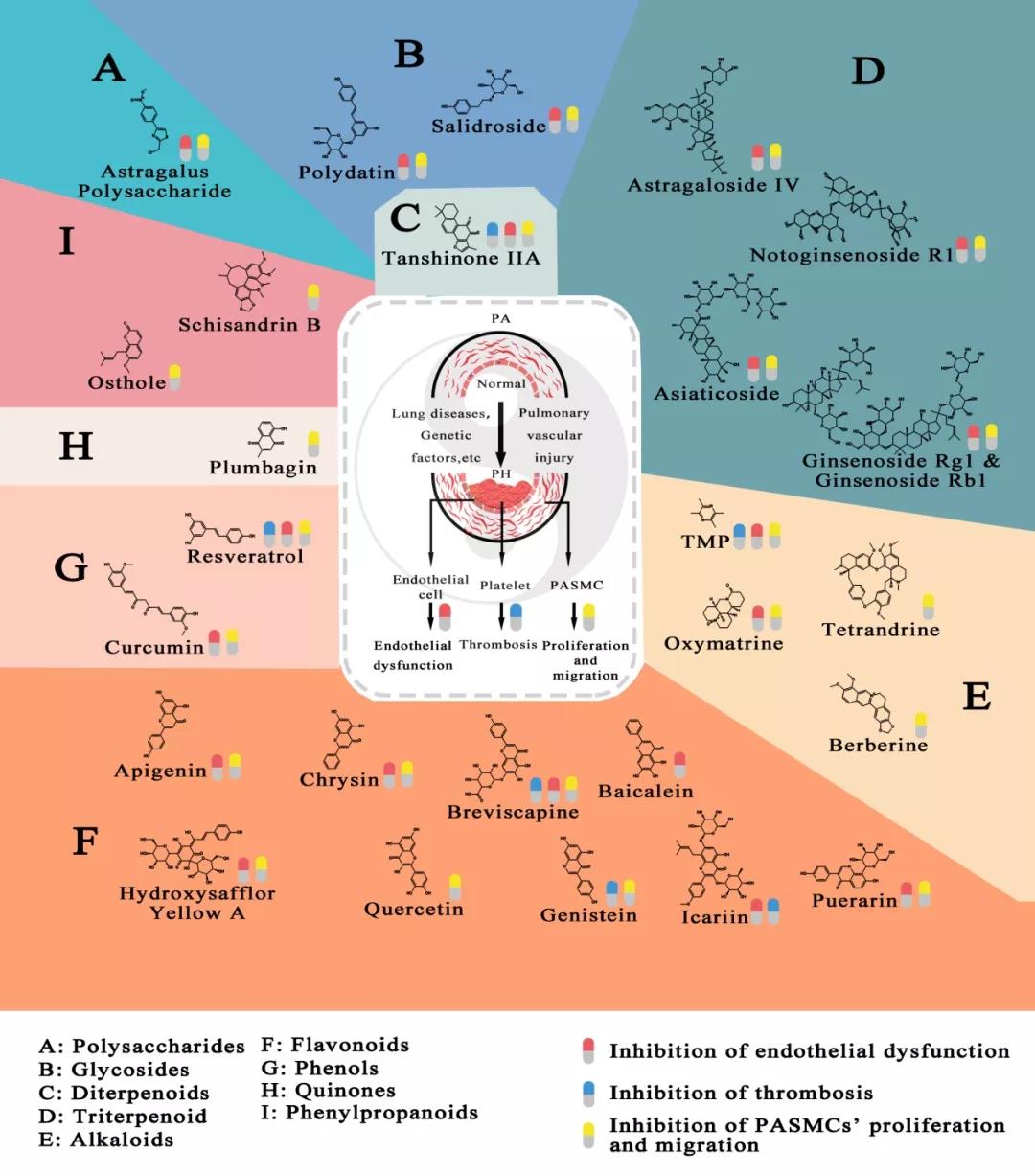
Fig. 1 Chemical classification of natural drugs from Chinese medicines and their pharmacological actions
(1) Polysaccharides
Astragalus polysaccharide: Extracted from astragalus. By promoting the synthesis of endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) and the secretion of NO, it promotes the vasodilation and suppresses pulmonary vascular remodeling, thus reducing the mPAP in rats with PH induced by MCT and reducing right ventricle hypertrophy.
(2) Glycoside
Resveratrol: Extracted from the roots and stems of giant knotweed. Researchers have found that resveratrol can significantly inhibit the proliferation and migration of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) and the generation of AngII and ET-1 in the model of rats with PH induced by hypoxia, while stimulating the NO synthesis in blood and lung tissues under hypoxia. All of these have together inhibited pulmonary remodeling and right ventricle hypertrophy.
Rhotinine: A main active ingredient extracted from rhodiola. In recent years, it has been found to have pharmacological actions such as anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, and immunity enhancing. Similarly, rhodiola has been observed with positive effects for plateau related symptoms and acute exacerbation of PH. In addition, rhodiola can improve the rats with PH induced by chronic hypoxia, inhibit the proliferation of pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs) induced by chronic hypoxia and reverse apoptosis resistance. Besides, PASMC apoptosis can be promoted by A2aR related mitochondria-dependent pathway. PASMC proliferation induced by platelet derived growth factor (PDGH)--BB by protein kinase B (Akt)/GSK3β signaling pathway, thus alleviating the chronic hypoxia-induced PAH.
(3) Diterpenes
Sodium tanshinone IIA: An effective ingredient of Salvia miltiorrhiza. It can effectively reduce the mPAP, right ventricular pressure and right myocardial hypertrophy index in the hypoxia-induced PH rat model and the MCT-induced PH rat model, and can also promote the increase of pulmonary blood flow in the PBF-induced PH rat model. In the rat models, it can inhibit pulmonary small vascular remodeling, protect the vascular endothelium, inhibit the PASMCs proliferation and migration, inhibit anti-inflammatory reaction, reduce platelet aggregation of pulmonary blood vessels and ultimately reduce myocardial hypertrophy. The specific mechanisms are related with the regulation of cellular potassium channel, intracellular calcium hemeostasis and cell cycle. Meanwhile, improvements in PH diagnosis have also been observed in PH patients given sodium transhinone IIA sulfonate (STS) or STS in combination with sildenafil, including 6-minute walk distance (6MWD), Borg breathing difficulty score, and PASP and right ventricular size measured by echocardiography.
(4) Triterpenes
Astragalus methyloside: Extracted from astragalus. It has been proven to be beneficial to the immune system and be able to reduce blood pressure, etc. In hypoxia-induced PH rats, it can improve the PH by means of inhibiting ET-1, AngII and PASMCs, etc.
Syracabin: It is the main active ingredient extracted from Centella. It can antagonize the effects of eNOS inhibitor, and thus contribute to the NO production, thereby inhibiting the hypoxia-induced abnormal endothelial cell apoptosis and the hypoxia-induced over-active transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)/ Smad2/3 signaling path. Besides, it can also promote PASMCs apoptosis, thereby dilating pulmonary vessels, inhibiting pulmonary vascular remodeling, and ultimately reducing mPAP, and reversing the right ventricular hypertrophy of rats with hypoxia-induced PH.
Ginsenosides Rg1 and Rb1: Ginsenoside Rg1 and Ginsenoside Rb1 have shown positive effectives in the prevention and treatment of PH. It has been found that Ginsenoside Rg1 can relieve myocardial remodeling by improving the expression of matrix metalloproteinase 2 (MMP-2) and MMP-9 in chronic thromboembolic PH rats. It can also inhibit the pulmonary vasoconstriction caused by hypoxia and hypercapthemia by inhibiting p38 in vitro. Besides, Ginsenoside Rb1 can also reduce the ET-1 induced PA contraction by inhibiting SOCE.
Notoginseng saponin: Extracted from notoginseng. Notoginseng saponin R1 can reduce the hypoxia-induced pulmonary vasoconstriction by reducing the expression of PASMC regulatory protein kinase (ERK) and p38. Besides, systemic administration of Notoginseng saponin R1 can significantly reduce the vascular endothelial hyperplasia after acute vascular injury in Guinea pigs, and inhibit the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) by inhibiting the activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway. It has also been proven that its intestinal metabolites can inhibit the proliferation and migration of VSMCs by blocking PDGF-BB induced G0/G1 phase VSMCs, thereby reducing intimal hyperplasia after carotid artery injury in the rats.
(5) Alkaloid
Ligusstrazine: Extracted from chuanxiong. It is widely used in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in China and has been found to have the functions such as protecting the vascular endothelium, inhibiting oxidative stress, inhibiting the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells, and inhibiting thrombosis. In vitro studies have shown that it may be involved in the regulation of extracellular signaling regulatory kinase and the P38-MAPK pathway, thereby inhibiting the PDGF-BB induced proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. In vivo, pulmonary vascular leakage was reduced in rats treated with Tetramethylpyrazine (TMP) and VEGF expression was down-regulated, especially in the hypoxia induction factor--1α (HIF-1α). TMP had therapeutic effects in all three rat models of chronic hypoxia induced PH, MCT induced PH and SU5416/hypoxia (SuHx) induced PH. In addition, some studies have observed the PH treated with ligustrazine <span style="text-indent: 0em; caret-color: red; font-family: "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, "Hiragino Sans GB", "Apple Color Emoji", "Emoji Symbols Fo