SKLRD co-develops a fast detection kit for novel coronavirus IgM antibody
2020-02-141705Recently, under the guidance of academician Zhong Nanshan, the SKLRD worked with four organizations including Guangzhou Regnerative Medicine and Health Guangdong Laboratory, Guangzhou Institute of Biomedicine and Health Chinese Academy of Science, Guangdong Hexin Health Tech Co., Ltd., and Guangzhou Enbao Biomedicine Tech Co., Ltd. to develop a fast detection kit for novel coronavirus IgM antibody, which has finished the initial evaluation in the Lab and clinically.
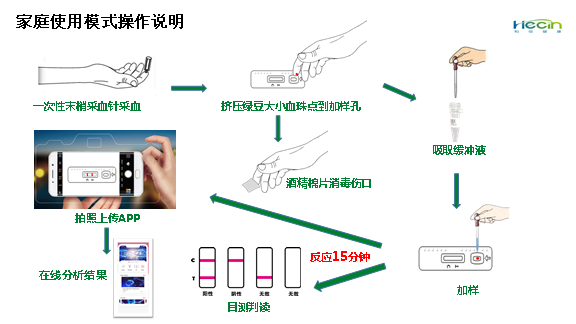
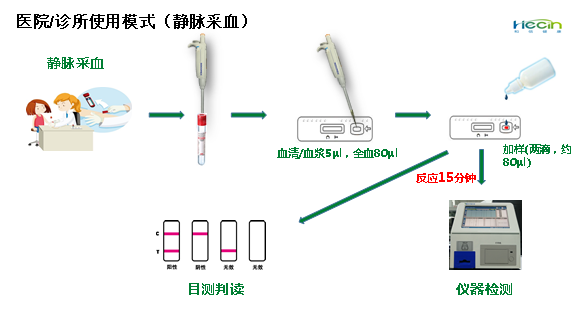
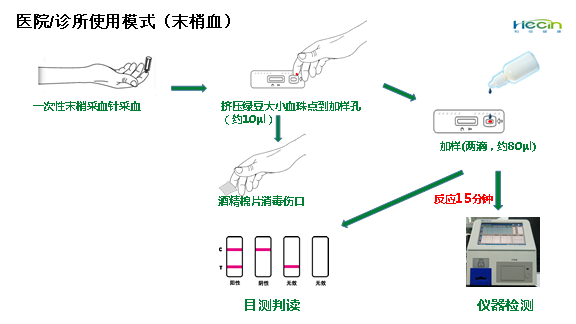
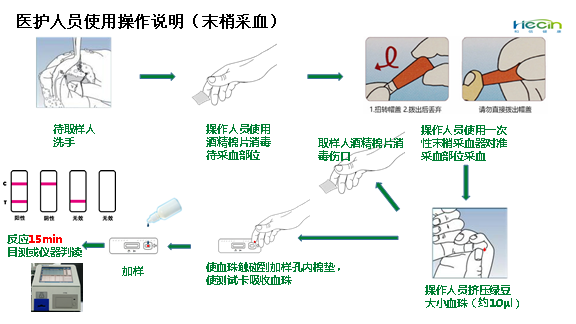
The kit applies colloidal gold immunochromatography technology and indirectly detects the IgM antibody of novel coronavirus. With a drop of blood, it can offer the detection result through naked eye observation in 15 minutes. After the plasma of the patient is diluted by 500 to 1,000 times, it can still detect the positive stripe. Compared with the existing RT-PCR nucleic acid detection used in diagnosis, the kit is simpler and more effective, with a higher sensitivity and specificity, which can effectively break the limitations of existing detection technologies to personnel and location, shorten the detection time, realize a fast diagnosis of suspected patients and an on-site screening of close contacts, and push the diagnosis and screening forward and downward.
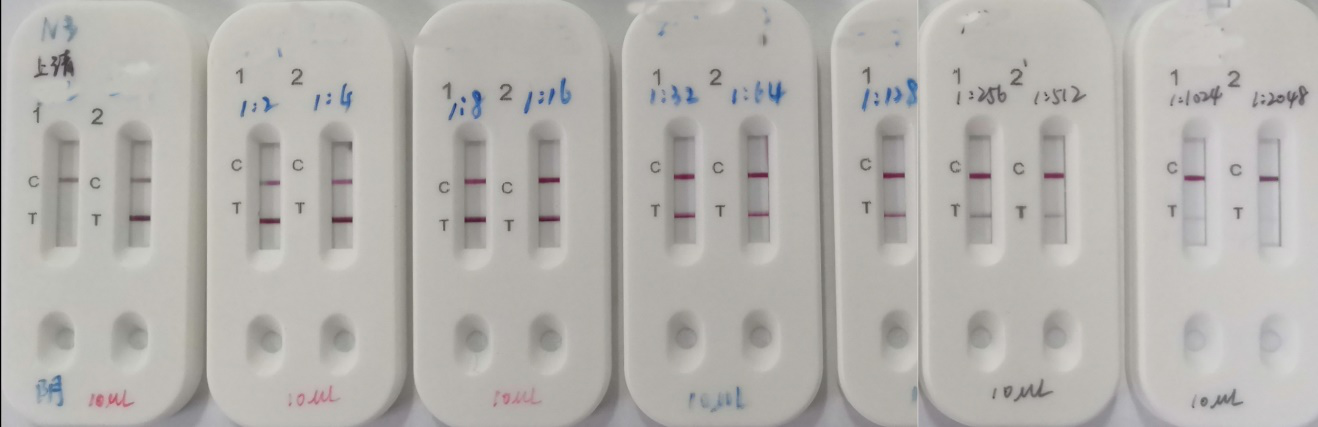
The kit has been put into a trial application at a hospital of Hubei. Through re-inspecting the blood samples of some patients who have been confirmed clinically as positive in novel coronavirus infection (yet confirmed as negative in PCR nucleic acid test), the kit can detect a large number of (IgM) positive cases, which implies that the kit can be used to supplement the nucleic acid test. Meanwhile, in the detection of over 600 clinical samples taken from Hubei and Guangzhou, the (IgM) positive detection rate of the kit shows a high consistency with the results of clinical diagnosis.
Currently, lots of samples of the kit (used for scientific researches) have been delivered to grassroots health institutions in places such as Wuhan, Huanggang and Daye of Hubei Province, which is used together with technologies such as nucleic acid test in the testing and evaluation of novel coronavirus infection detection.