Experts of SKLRD reveal the molecular mechanism of treatment of COPD with NaHS
2019-11-181121Recently, the team led by Professors Lu Wenju and Wang Jian of the SKLRD has achieved a new progress in its research on the mechanism of the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) with NaHS. The related research findings were published in the academic journals International Immunopharmacology (IF:3.361), Aging-US (IF:5.515) and Redox Biology (IF: 7.793) successively in 2019.
COPD is one of the four major chronic diseases, which is a kind of chronic and lethal pulmonary disease and is in urgent need of new preventive strategies and treatment medicines clinically. There are about 100 million patients of COPD in China. NaHS is a donor of H2S. Multiple researches have proven that NaHS can relieve the pathological changes of COPD model triggered by cigarette smoke (CS), improve the lung functions of animals, yet its mechanism is still unconfirmed. After over five years of series researches, the team led by Professors Lu Wenju and Wang Jian have successively revealed the molecular mechanism for treatment of COPD with NaHS, which has provided theoretical support for the clinical application research of treatment of COPD with NaHS and the research and development of new effective drugs for the treatment of COPD.
I. H2S improves emphysema and airway wall reshaping by regulating the functions of mitochondria
NaHS can generate H2S in the body to activate the SIRT1 to relieve the ageing and death of alveolar epithelial cells caused by the disorderly mitochondria and improve the oxidative stress of the lung. Meanwhile, NaHS can also improve the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and collagen deposition of bronchial epithelial cells and airways of mice caused by exposure to cigarette smoke, thus improving the airway reshaping triggered by CS.
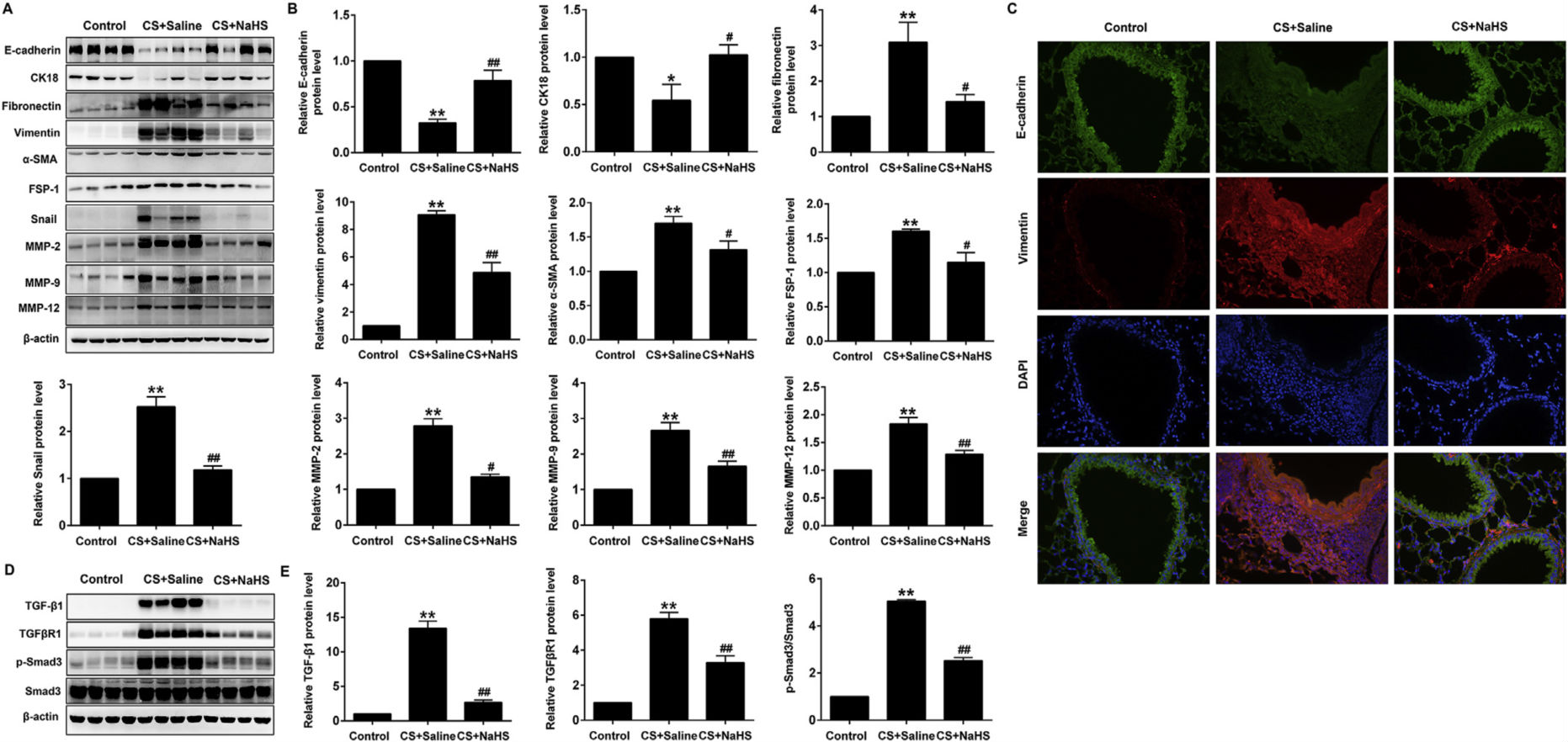
Picture 1 NaHS can improve the airway EMT, collagen deposition and reshaping caused by exposure to cigarette smoke
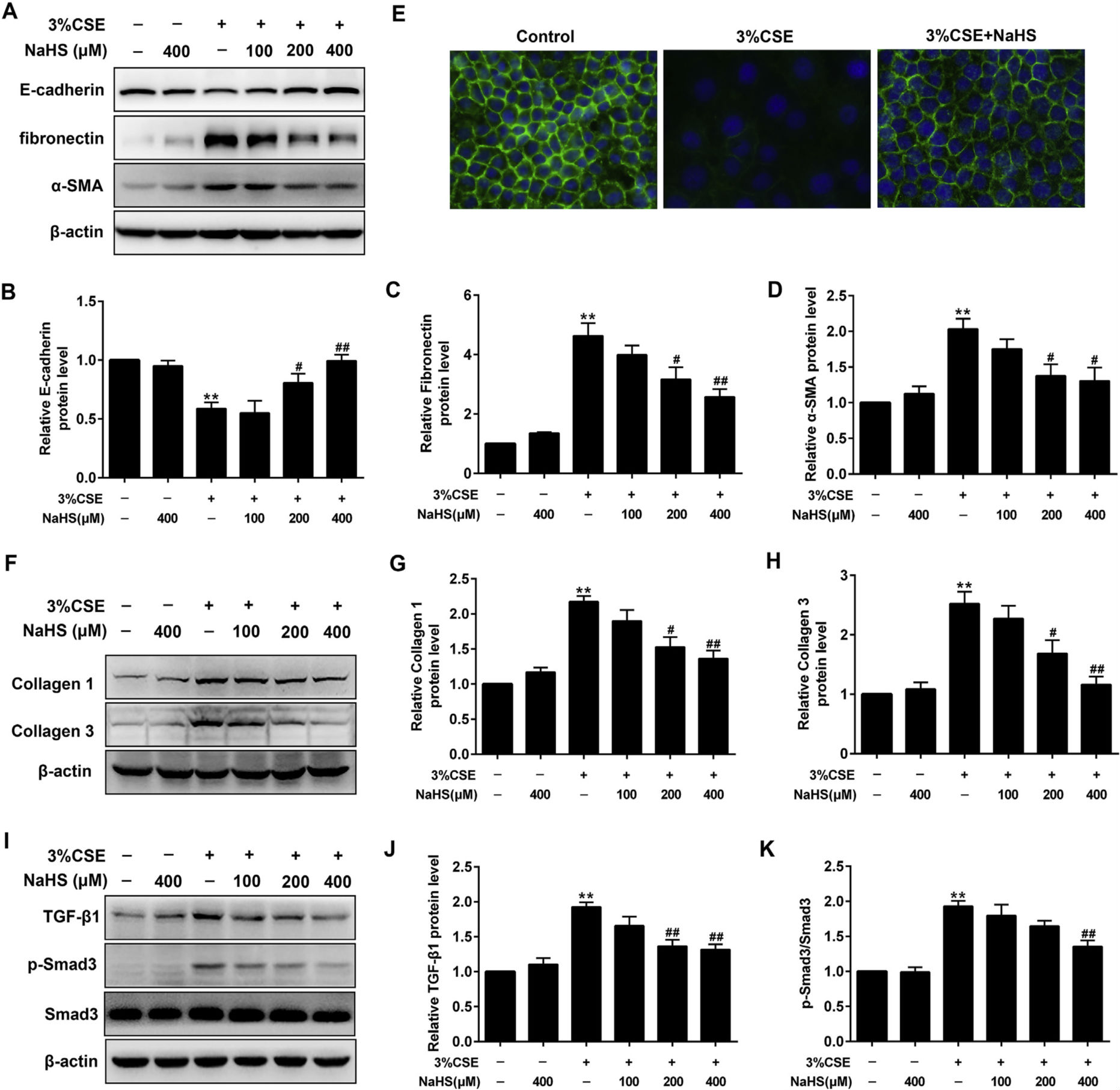
Picture 2 NaHS can improve the EMT, collagen synthesis and oxidative stress level of bronchial epithelial cells 16HBE caused by exposure to CS extract
II. NaHS can inhibit airway inflammation and emphysema by regulating the signal transduction mediated by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1α)
The researchers also discover that NaHS can inhibit the inflammatory reaction caused by exposure to CS (or CS extract) by regulating the signal channel of PHD2/HIF-1α/MAPK, thus inhibiting the damage and death of alveolar epithelial cells and preventing emphysema and improving lung functions.
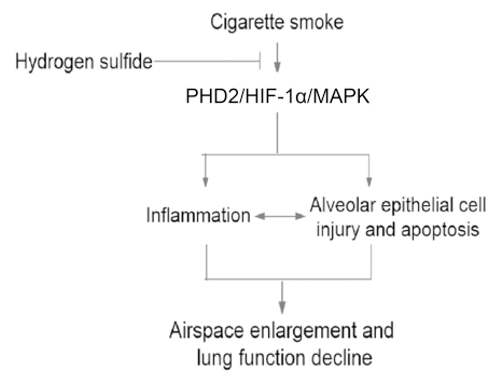
Picture 3 The schematic diagram of the mechanism for NaHS to inhibit inflammatory reaction triggered by CS